CCDC announces 2020.0 CSD Release
Scaling up structural science
Cambridge UK, 12th December 2019. CCDC, world leading providers of structural chemistry data for material and life sciences, today announced the 2020.0 CSD Release, offering improved visualisation and extraction of data driven insights from now over one million structures in the Cambridge Structural Database.
After celebrating the huge milestone for structural chemistry with the addition of the millionth structure to the CSD in June 2019, this release continues the strong growth towards the next million. The 2020.0 CSD Release contains 1,034,174 entries and 1,016,168 unique structures; an increase of more than 60,000 entries to the CSD compared to the 2019.0 CSD Release.
Alongside the increase in the scale of the CSD itself, the 2020.0 CSD Release provides a range of new capabilities to users working within all areas of structural science, as well as improved user experience for licence holders.
For users of CCDC’s CSD-Materials suite, this release provides quick and easy hydrogen-bond likelihood analysis with new H-bond Coordination Quick-View, which enables users to quickly assess the likelihood of hydrogen-bonding behaviour purely on coordination numbers for the loaded model. The coordination outcomes observed in a crystal structure often provide a useful indicator of structural stability, or a warning flag for metastability, so this new component helps make a fast assessment of that aspect of the structure.
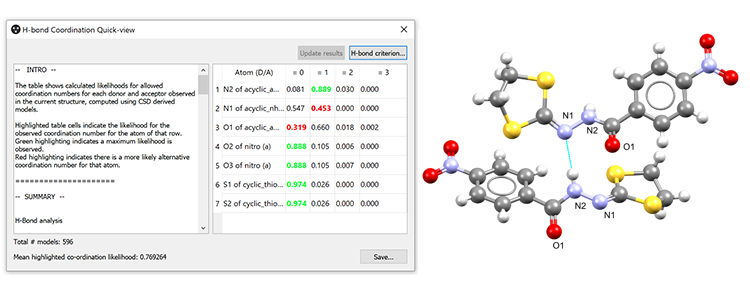
H-bond Coordination Quick-View
One of the most profound updates for users of CSD-Discovery is in the scale-up potential of CCDC’s protein-ligand docking component – GOLD. The deployment options for GOLD have been optimised so that users can now tackle ultra-large docking projects with GOLD’s world-class docking algorithm. Using fast settings on cloud architectures, with automated selection of the best scoring results, this allows docking of tens of millions of compounds in timescales convenient for structure-based drug design programmes. The chemical space of drug-like molecules is vast, but this approach allows users to effectively screen a very wide space of potential drugs whilst retaining most of the accuracy of GOLD.
CCDC have also announced that as part of this release they would be moving the CSD Python API as standard to Python 3. The CSD Python interface, providing programmatic access to both CSD data and CSD functionality, has democratised the use of the validated, curated information and methods, allowing scientists to build their own tailored workflows and applications as well as integrate more easily with other software packages. In the last year the CSD Python API enabled research into the structure and properties of indomethacin co-crystals, evaluation of force-field calculations on lattice energies and the development of new accurate geometrical restraints for Watson-Crick base pairs. By incorporating Python 3 by default, the CSD Python API will be Python 3 enabled straight away at the point of installation and easy to integrate with other key scientific Python packages like TensorFlow, scikit-learn, matplotlib, pandas and RDKit allowing users to harness the potential of these libraries alongside CSD data and software.
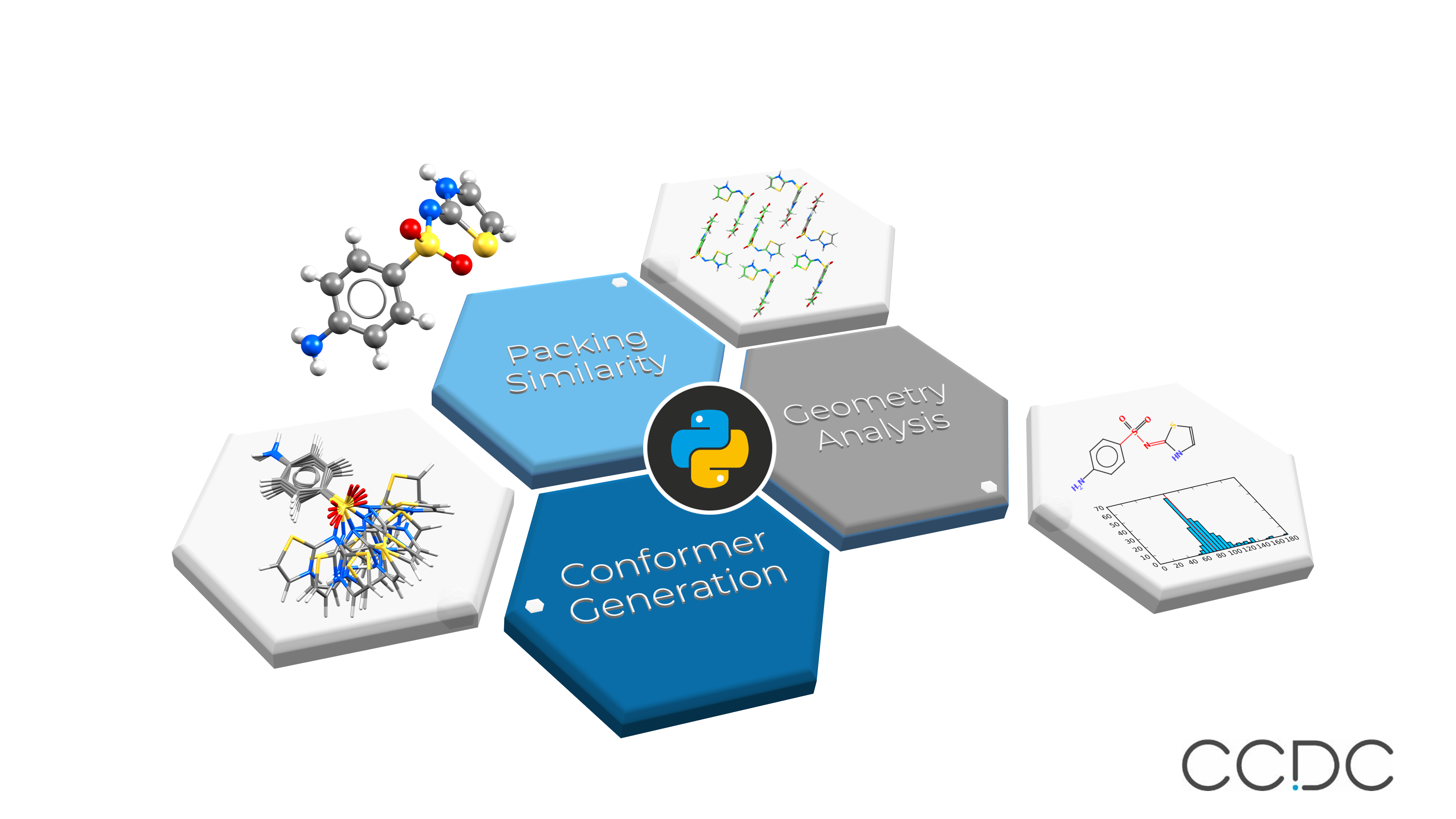
An overview illustrating various types of structural reporting and analysis enabled by the CSD Python API
Alongside updates to their software throughout 2019, CCDC have also been looking at implementing more effective, data-driven decision-making in their product strategy and development throughout 2020 and beyond.
CCDC’s data and software is used in almost every chemistry department in the world, as well as within many pharmaceutical and chemical companies to drive drug discovery projects and materials development. Despite this, the centre has previously lacked visibility of the intensity of demand for the individual tools within their software suites. Therefore, as part of the 2020.0 CSD Release, CCDC have announced the implementation of an entirely opt-in Product Telemetry system within their software, which allows them to capture information about their tools including frequency of use and types of operating system.
“Introducing product telemetry within our software will help us access the data we need to inform the direction of our product roadmap in 2020 and subsequent years, helping us streamline our in-house processes and productivity and ultimately provide our users with what they most need,” commented Pete Wood, Senior Product Manager at CCDC. “We would also like to emphasise that this system is entirely opt-in and this data is anonymous. We won’t capture information such as usernames, IP addresses, site information or e-mail addresses, and we won’t analyse what the user is doing, only which software component has been used.”
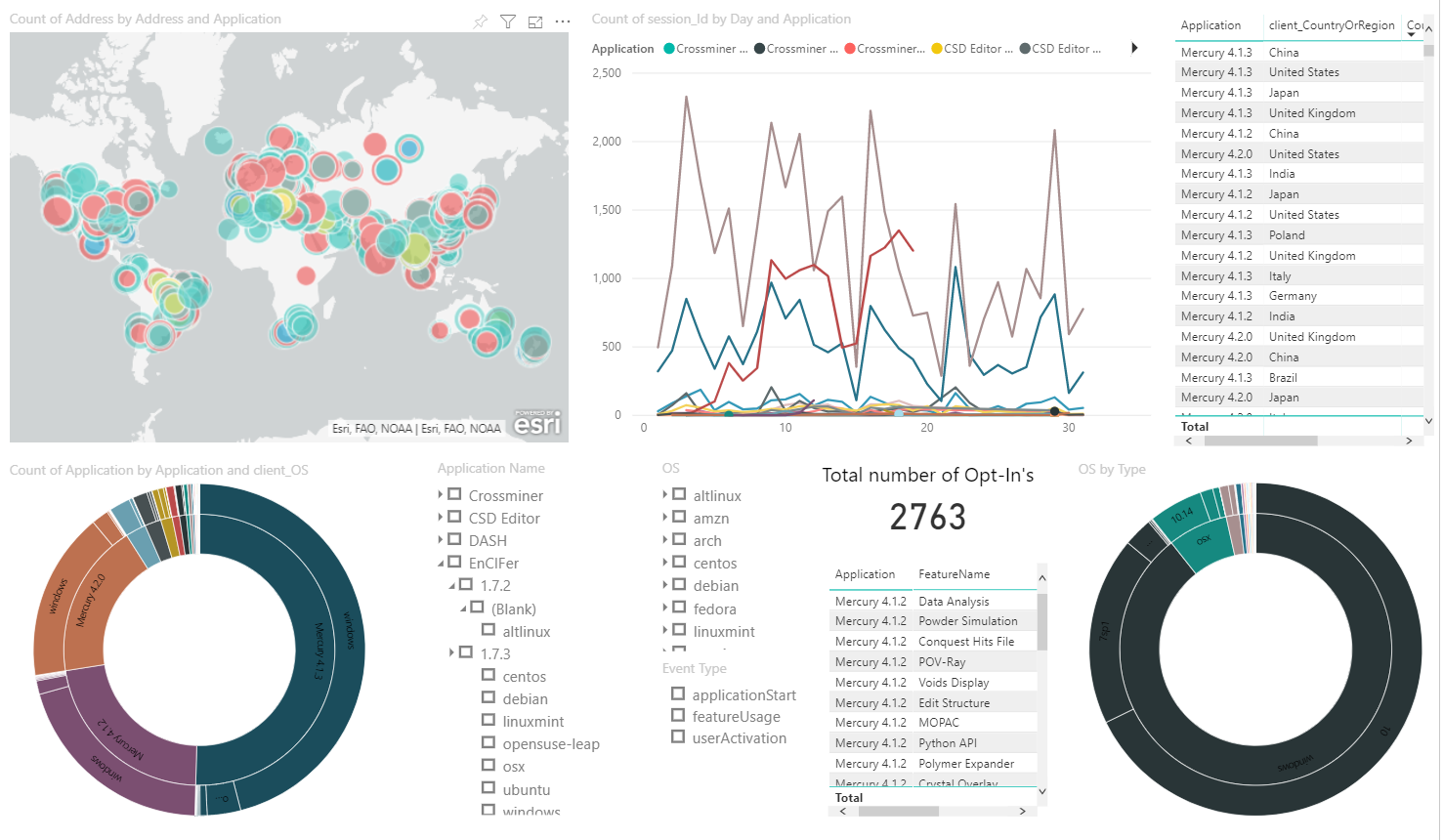
Generating insights from application data
Improving user experience, outside the provision of just their tools, is always a key priority for CCDC. The 2020.0 CSD Release offers substantial improvements to user experience with the announcement of a new licensing system, providing licence holders with more flexibility and easier access to the software.
CCDC’s current licensing system is over 20 years old and has many limitations including restrictions to a yearly release cycle and limiting the licence of individual components. This new system is modern, secure and regularly updated, allowing both online and offline activation, therefore providing flexibility for users as well as enabling CCDC to play to their strengths and concentrate on delivering continuous improvements in their scientific software and data.
Dave Bardwell, Support Team Leader, commented “A new licensing system is long overdue for CCDC, we are excited to be rolling out such a modern flexible system which will make life easier for both our licence holders and our CCDC support team. We also have some further plans to improve access, including access to an online portal to both manage, and purchase, extend and upgrade licences, which will be announced in subsequent releases throughout 2020.”
Juergen Harter, CEO at CCDC said, “2019 has been an exciting and fast paced year for CCDC. As well as hitting the milestone of one million structures in the CSD, we’ve been working hard on changing the way we work as a centre, ultimately to improve what we deliver to the structural science community.
This release provides some great headway for CCDC as we move into 2020 and we will continue to look into new ways of working to ensure we deliver the community the high-quality data and the most valuable tools required to advance their research in 2020 and beyond.”