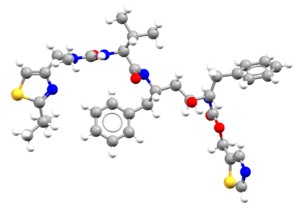
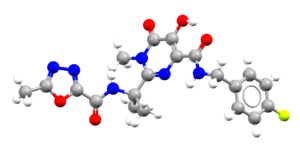
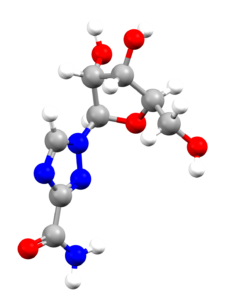
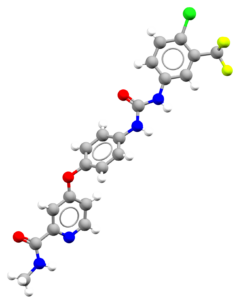
Explore the Ligand Cards
Welcome to the Bound! drugs page, where you will learn more about the drugs that you are using in the Bound! card game.
Bound! is the protein-drug matching game that has you match protein cards (targets) with ligand cards (drugs): match the most pairs to be the winner!
The pair selected for this game are chosen at the intersection of two databases of crystal structures:
- The proteins (targets) are from the Protein Data Bank (PDB), a repository of 3D biolmolecular structures central to research and education.
- The ligands (drugs) are from the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD), a database of over 1 million curated small-molecule organic and metal-organic structures, curated by the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC).
In this page you will explore the drug structures from the CSD, if you are looking for the cards deck and the game rules, click on the button below to go back to the main page.
Go back to the rules and cards
The Bound! Drugs
In each panel you will find:
- The drug common name.
- The CSD Refcode (what is a refcode?) with a link to the structure entry in the database, via our search tool Access Structures. In each structure page you will find more information and a 3D interactive representation. You can find a quick explainer on how to use the result viewer in Access Structures, if you need help in navigating the visualizer.
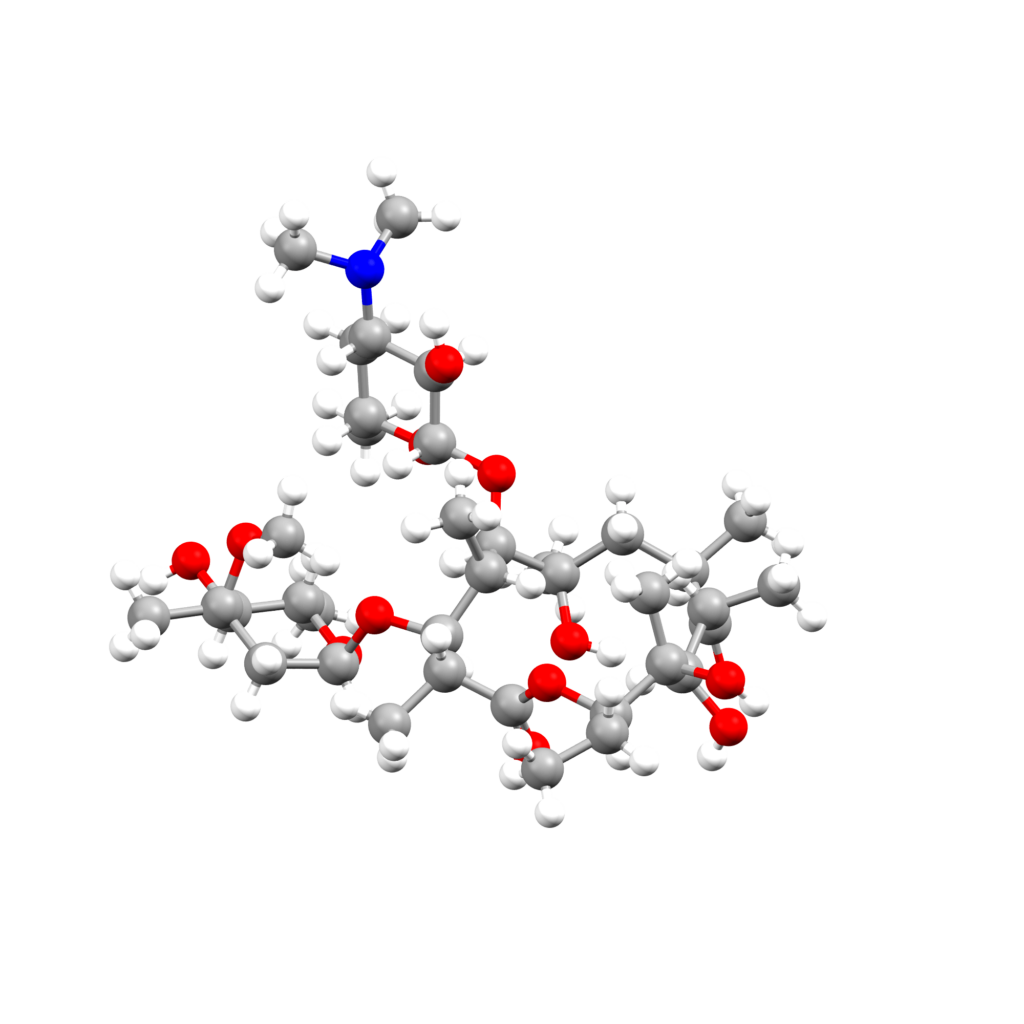
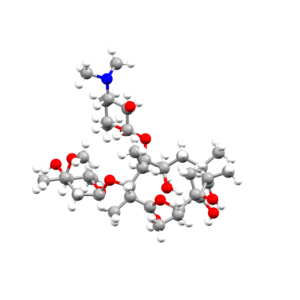
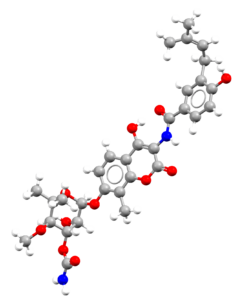
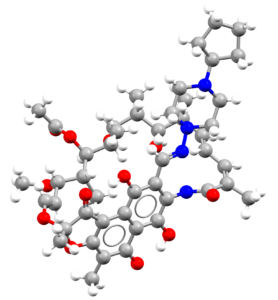
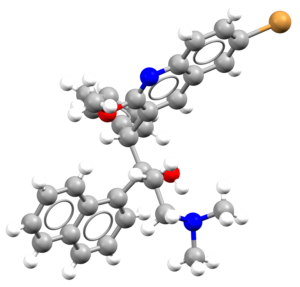
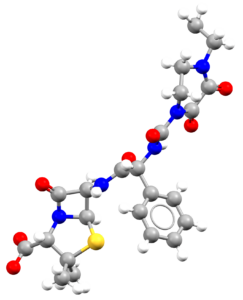
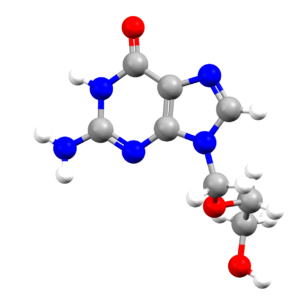
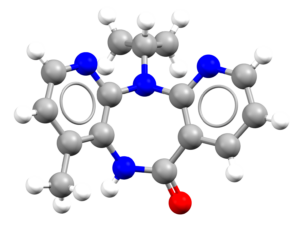
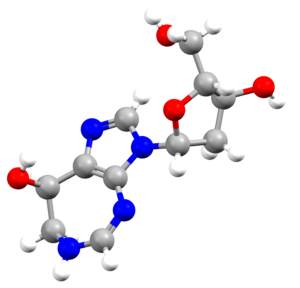
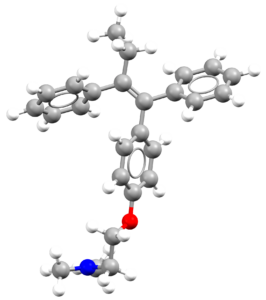
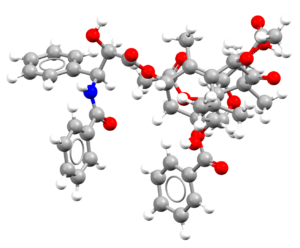
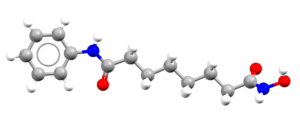
- An image of the drug molecule, created with the free version of the CCDC’s visualization software Mercury. You will find below a legend reporting the elements colours used in the representation.
- An interesting fact about the drug.
- The mechanism of action, which you can find explained on the right.
- The protein the ligand binds to, indicated with its PDB codes linking to the protein (target) entry in the Protein Data Bank.
Atom colours legend
Carbon – Grey, Hydrogen – White,
Nitrogen – Blue, Sulphur – Yellow,
Oxygen – Red, Fluorine – Lime Green,
Bromine – Brown, Chlorine – Green
Mechanisms of Action
The term mechanism of action refers to the specific interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. The drug cards have a mechanism of action included.
-
Inhibitor – A substance that binds to a target to reduce the target’s activity
-
Antagonist – A drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it (opposite is agonist)
-
Agonist – An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response
-
Activator – A DNA-binding protein that regulates one or more genes by increasing the rate of transcription
-
Potentiator – A substance that enhances sensitization of an antigen
-
Inducer – A molecule that regulates gene expression
-
Modulator – A drug that binds to receptor at a different site from where an agonist binds and influences the function of the receptor