Investigation of Interactions in Organometallic Compounds Using GOLD
This blog highlights the use of the protein–ligand docking tool GOLD to investigate organometallic compound interactions and the use of Mogul to perform structural validation. The full work can be accessed here: Dalton Trans., 2023, 52, 11859-11874.
Introduction
Antimitotic agents are important drugs in anticancer therapy. Owing to their strong side effects and the development of resistance, scientists are searching for more selective antimitotic drugs exhibiting a lower systemic toxicity.
Kinesins are proteins involved in mitosis that are particularly important targets for therapy. New kinesin spindle protein (KSP) inhibitors have been explored and discovered, and ispinesib is one of those. As the most promising results in clinical trials were obtained by combining ispinesib with capecitabine and carboplatin, the scientists started investigating other metal-based drug candidates.
Introducing an organometallic moiety, such as sandwich compounds of Fe and Ru, or half-sandwich compounds of Ru, Os, Rh and Ir, into the structure of an organic pharmacophore often enhances its biological activity. Important advantages can derive from the use of organometallic compounds: they achieve structures that can’t be obtained by using organic scaffolds only; the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) detrimental to the cell is more likely to occur when in the presence of an organometallic moiety.
Proceeding with their work on Rh and Ir half-sandwich complexes that exhibited high KSP inhibitory activity, the group investigated the effect of combining ispinesib and half-sandwich complexes into the same molecule on the biological activity.
Results and Discussion
The synthesis of the organometallic complexes was performed starting from the (R)- and (S)-enantiomers of ispinesib. Those precursors were reacted with 2-pyridinecarboxaldehyde in ethanol to form the (R)- or (S)-imines, and then with the metal dimers to form the half-sandwich conjugates of ispinesib. The metal dimers used were [(cym)MCl2]2 (M = Ru, Os; cym = η6–p-cymene), [(1,3,5-iPr3C6H3)RuCl2]2 or [(Cp*)MCl2]2 (M = Rh, Ir; Cp* = η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl).
The characterization of the products was performed with NMR spectroscopy, elemental analysis, and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (ESI-MS). For the Ir-based complex, the crystal structure was also obtained via single crystal X-ray diffraction (Figure 1).
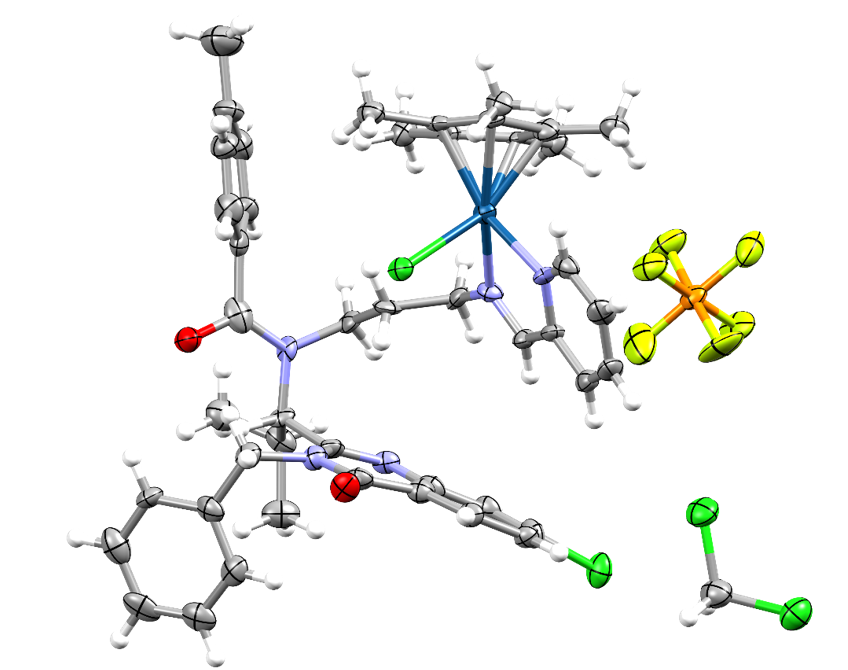
The Ir compound reported in Figure 1 crystallizes in the P21 space group in a monoclinic crystal system. The asymmetric unit consists in the Ir complex with a PF6‒ counterion and a co-crystallized molecule of the solvent CH2Cl2. The metal centre displays a pseudo-octahedral geometry, where the imine and pyridine-2-yl moieties coordinate to the Ir ion as a N,N-bidentate chelator, forming a five-membered ring. A chlorido ligand and a η5-pentamethylcyclopentadienyl ligand also coordinate to the metal centre, completing its coordination sphere.
The group performed a geometry check against the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD) for the Ir half-sandwich conjugate of ispinesib using Mogul, a CCDC tool to validate experimental crystal structures. The parameters found in the experimental structure did not differ significantly from the ones of other deposited structures. The bond lengths for the Ir surrounding and dihedral angles were in fact close to those found in Ir complexes with a similar structure, confirming the reliability of the experimental results.
All the synthesized compounds showed antiproliferative potential in the micromolar or submicromolar range, exhibiting higher bioactivity compared to the parent compounds (the (R)- and (S)-enantiomers of ispinesib).
The group also performed docking studies using the protein–ligand docking software GOLD. The complexes were docked at the ispinesib binding site of human kinesin KSP and compared to that of the parent compounds. It was seen that when the complexes were docked, the N,N-bidentate ligands occupied an inner hydrophobic region of the binding pocket, while the metal-based moiety was placed in a hydrophilic region. The configurations of the complexes differ from the ones of the (R)- and (S)-enantiomers of ispinesib, allowing the formation of π-interactions with important residues such as Trp127 and Tyr211.
Conclusions
A new series of half-sandwich conjugates of ispinesib exhibiting high bioactivity was designed and synthesized. The crystal structure of one of the conjugates was obtained and validated using Mogul. The group performed docking studies using GOLD, and investigated the interactions of the docked organometallic complex.
Next Steps
To discuss further and/or request a demo with one of our scientists, please contact us via this form or .
Read the full work: Dalton Trans., 2023, 52, 11859-11874.