How to use the Aromatics Analyser
The Aromatics Analyser feature was released in our 2020.1 update, as part of the CSD-Materials suite. This short video shows you how to use this feature, and how to interpret the results.
You can also follow the self-guided pdf workshop on how to use and interpret results in Aromatics Analyser here.
Why are aromatic interactions important?
Hydrogen bonds may not always be enough to fully understand the structure of a molecule. For example, in the image below we see that two polymorphs of ibuprofen show just one point on a hydrogen bond propensity map.
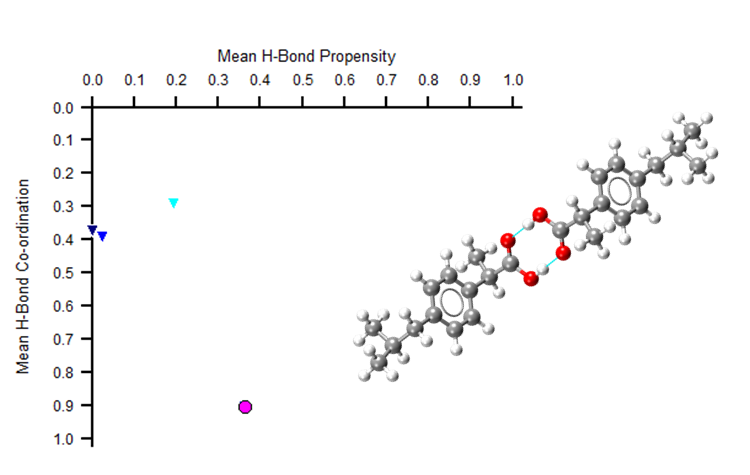
The pink circle shows how two polymorphs of ibuprofen appear at the same point on a hydrogen bond propensity map – showing how this analysis alone may not fully characterise your molecule.
This means that a second polymorphic form could be missed. By additionally assessing the aromatic interactions, we can distinguish between polymorphs.
How does the Aromatics Analyser work?
The analyser applies a Machine Learning algorithm to generate a model using molecular descriptors (eg.: atom-atom distance, centroid to centroid distance) and DFT energies of all possible orientations of benzene dimer pairs.
This is all used to estimate the strength of the interactions.
You can learn more about the neural network methods used to build the analyser in my blog post here.
How can I access the Aromatics Analyser?
This feature is included in the 2020.1 release of CSD-Materials and CSD-Enterprise suites.
Contact us here if you don’t currently have access but want to try this feature.