CSD in Action: Next Generation Ovarian Cancer Drug Identified by GOLD Virtual Screening and Confirmed Experimentally
Researchers at Yale University School of Medicine and Emory University School of Medicine have used CCDC’s protein-ligand docking software GOLD to identify a promising next generation ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) inhibiting candidate for the treatment of ovarian cancer (that was then validated experimentally) from a starting pool of over 200,000 compounds.
This is part of our series highlighting examples of the Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC) tools in action by scientists in industry and academia.
Reporting in Scientific Reports,1 the team used GOLD to investigate docking of the triapine-binding pocket on RNR. Triapine had been previously shown by the researchers to be a promising drug (in combination with poly ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) inhibitors) for the treatment of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC).2,3
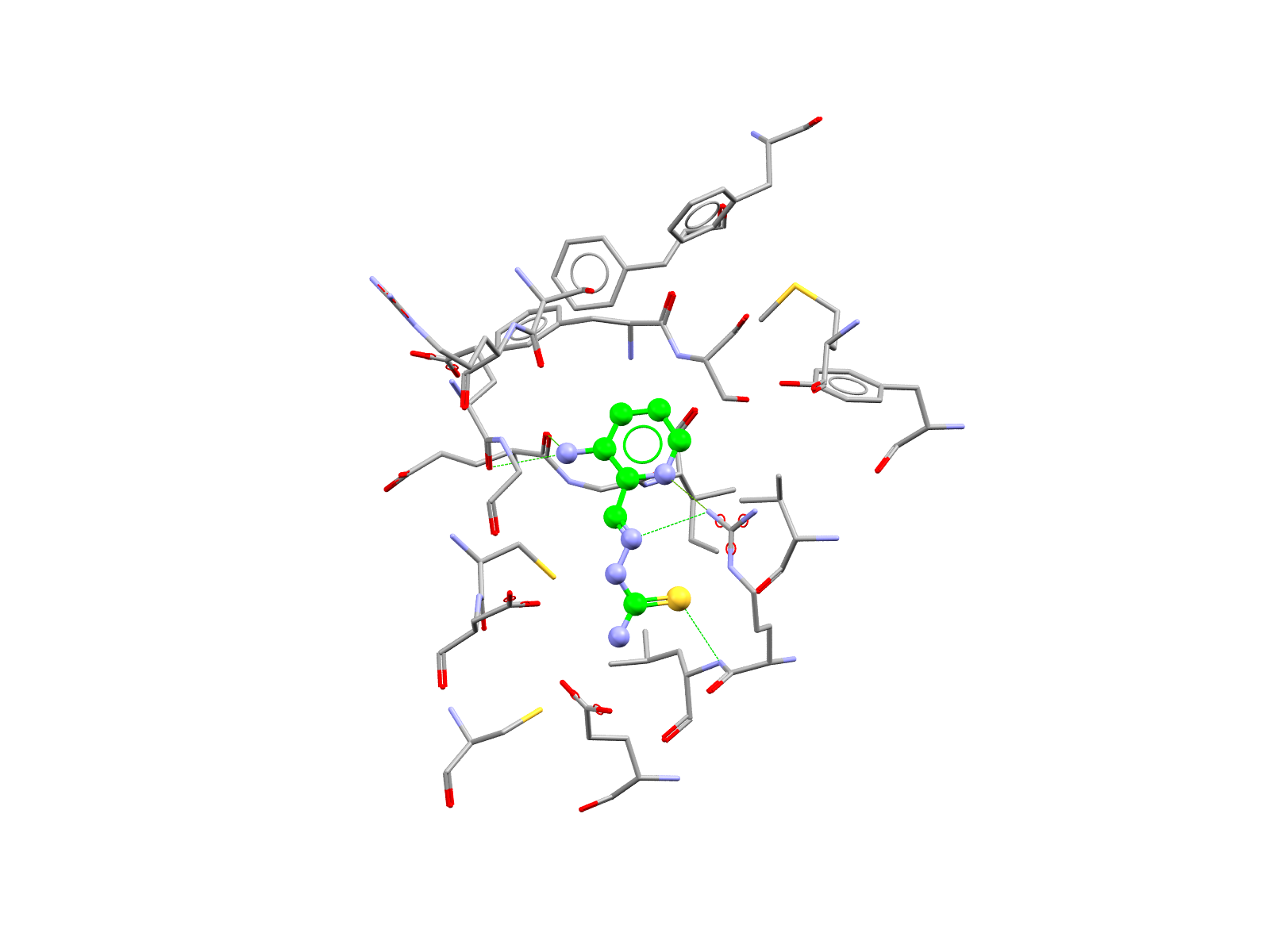 The triapine-binding pocket of the R2 subunit or RNR. Docking post of triapine in the cavity was modelled with GOLD.
The triapine-binding pocket of the R2 subunit or RNR. Docking post of triapine in the cavity was modelled with GOLD.
Why
PARP inhibitors have been clinically approved as treatment for EOC with BRCA gene mutations or defective homologous recombination (HR) repair.
However, BRCA mutation reversal and restoration of HR repair has resulted in the PARP inhibitors being less effective in their treatment.
A drug that targeted the HR repair would sensitize repair-proficient EOC to PARP inhibitors, restoring their effectiveness towards the treatment of EOC.
Virtual Screening of 200,000+ Compounds
Triapine, a known RNR inhibitor (and thus HR repair inhibitor), is known to be effective in the treatment of EOC. The scientists used virtual screening to investigate protein-ligand docking of the triapine-binding pocket on RNR to identify a next generation RNR-inhibiting candidate for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Virtual screening using GOLD of over 200,000 compounds revealed hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions with the triapine binding pocket. Hit-clustering was performed on the most promising 200 compounds, narrowing the candidate field down to 25 candidates.
Experimental validation and further physicochemical analysis identified a potential candidate.
A Powerful Combination
Use of this RNR and HR inhibitor in combination with a PARP inhibitor was shown in vivo to be a significant treatment against HR-repair proficient EOC.
“We performed in silico screening of libraries of 200,000 compounds using GOLD to identify small-molecule ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) inhibitors that block DNA repair and sensitize ovarian cancer to PARP inhibitors.
Twenty-five in silico hits were selected for experimental validation. The leads were identified with activities at 15-30 µM concentrations in cell-based assays. GOLD helped us explore the chemical space of RNR and discover a new class of RNR inhibitors that defies the issues of traditional iron-chelating RNR inhibitors.
Furthermore, GOLD allowed the enrichment of hit compounds for subsequent experimental validation, providing a much greater advantage than conventional high throughput screening. It certainly saved time and resources for our undertaking in drug discovery.”
– Dr Z Ping Lin, Yale University School of Medicine.
Next steps
Download the free whitepaper – ultra-large GOLD docking on cloud resources.
Find out more about the protein-ligand docking software GOLD used in this research.
Read more case studies, including drug discovery at Novartis, Roche, Merck and AstraZeneca.
View the GOLD user guide, tutorials and technical documentation.
References
1. Lin, Z.P., Al Zouabi, N.N., Xu, M.L. et al. In silico screening identifies a novel small molecule inhibitor that counteracts PARP inhibitor resistance in ovarian cancer. Sci Rep 11, 8042 (2021). Read online.
2. Finch, R. A. et al. Triapine (3-aminopyridine-2-carboxaldehyde- thiosemicarbazone): A potent inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase activity with broad spectrum antitumor activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 59, 983–991 (2000). Read online.
3. Finch, R. A., Liu, M. C., Cory, A. H., Cory, J. G. & Sartorelli, A. C. Triapine (3-aminopyridine-2-carboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazone; 3-AP): An inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase with antineoplastic activity. Adv. Enzyme Regul. 39, 3–12 (1999). Read online.