Technetium
Technetium:
Core facts about the element technetium.
Facts about Technetium:
- Technetium: Tc is the lightest element whose isotopes are all radioactive and is a shiny grey metal.
- Fun fact about Technetium: Technetium was missing in the original periodic table of Mendeleev. No isotope has a half-life greater than 4.21 million years i.e. less than the age of the Earth. It is a nuclear fission product.
- Chemical symbol: Tc
- Atomic number: 43
A crystal structure containing Technetium:
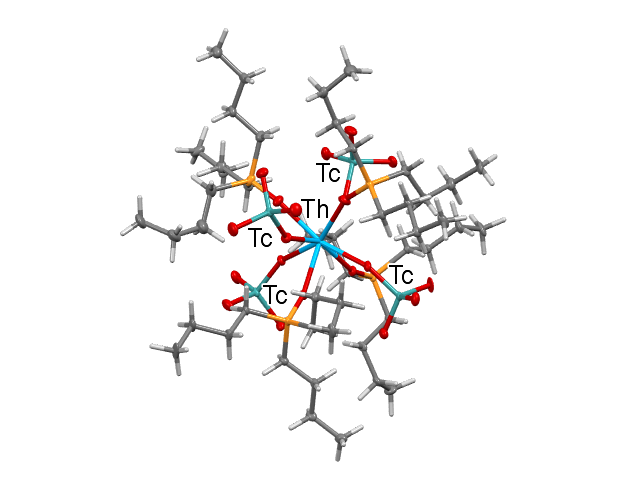
Representation of [Th(TcO4)4(TBPO)4].
Facts about this structure:
- Formula: C48 H108 O20 P4 Tc4 Th
- Structure name: tetrakis(Tributylphosphine oxide)-tetrakis(pertechnetate)-thorium(iv)
- Fun fact about the structure: The study revealed two reversible space group transitions as the temperature is reduced from 293 to 100 K, namely space groups I4 ̅3m, Cmc21 and Pbc21. This leads to a stepwise improvement of the order.
- CSD refcode: WAHQOM (What’s this?)
- Associated publication: Mark J. Sarsfield, Andrew D. Sutton, Iain May, Gordon H.John, Clint Sharrad and Madeleine Helliwell Chemical Communications (2004), 2320-2321., DOI: 10.1039/b404424j
More about Technetium:
Technetium lies between manganese and rhenium in group 7 of the periodic table, and its chemical properties are intermediate between those of these two adjacent elements. In 1937 Segrè and Perrier succeeded in isolating the isotopes technetium-95m and technetium-97. The most common naturally occurring isotope is 99Tc. In 1961, technetium-99 was first identified as a fission product of uranium-238 when it was isolated in very small quantities from African pitchblende. Technetium-99m (“m” means metastable) is used in radioactive isotope medical imaging. It is a gamma emitter with a half-life of 6.01 hours (meaning that about 94% of it decays to technetium-99 in 24 hours). This single isotope can be used for a multitude of diagnostic tests such as thyroid scanning. Technetium-99 is produced by the nuclear fission of both uranium-235 and plutonium-239. It is therefore present in radioactive waste and in the nuclear fallout of fission bomb explosions.
Learn More About the International Year of the Periodic Table (IYPT) in Crystals Project:
This project (#IYPTCrystals) is part of the International Year of the Periodic Table celebration (#IYPT2019), read more about the project here.
You can follow us on social media; search for #IYPTCrystals or follow The CCDC on X @ccdc_cambridge on Facebook ccdc.cambridge, on Instagram ccdc_cambridge or on YouTube CCDCCambridge.
Understand some of the terms and concepts used with our Frequently Asked Questions page here.
A 3D visualization showing Technetium in real crystal structures: