GOLD in Action: Virtual Screening to Repurpose Drugs for COVID-19
Here we highlight a paper which used virtual screening to identify drugs which could be repurposed to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 MPro (COVID-19). Part of our series highlighting examples of CCDC tools in action by scientists around the world.
Summary
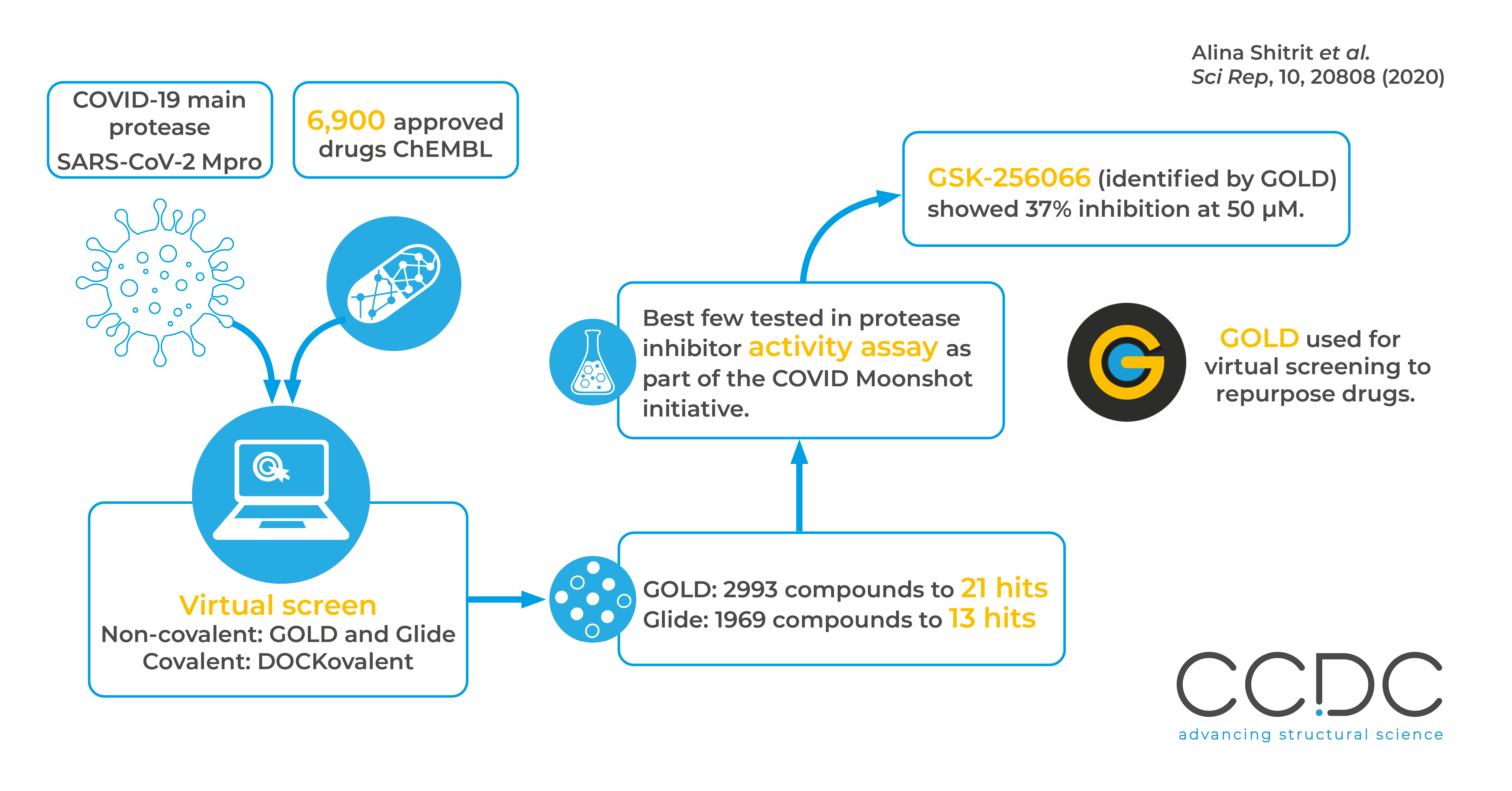
In this work in silico or virtual screening of a library of 6,900 approved drugs was performed to identify those which could be repurposed to inhibit the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). The leads identified went on to be tested in vitro and showed activity at ~50 µM concentration.
Why
Repurposing drugs offers a fast alternative to the lengthy, complex and uncertain process of novel compound discovery. This makes repurposing especially suited in a pandemic, where speed is essential to reduce loss of life. The first drug identified as an effective treatment of COVID-19 was a repurposed corticosteroid.
How
The ChEMBL database of drugs at various stages of clinical trials was filtered, and the resulting library screened in silico using non-covalent and covalent methods. GOLD was used in non-covalent virtual screening, and identified 21 hits. The lead compounds went on to be tested by protease inhibitor activity assay, as part of the COVID moonshot initiative. This found one compound, a molecule in phase 2 for treatment of COPD and identified by GOLD, showed 37% inhibition at 50 µM.
Read more
Read the Scientific Reports paper here.